Table of Contents
ToggleAccountancy is an ART of Recording, Classifying and Summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, financial transactions and events which are in part at least of a financial character and interpreting the result thereof.
“American Institute of Certified Public Accountant”
Non-economic activity is an activity performed with the purpose of rendering services to others without any consideration to financial gain. Example Mother cooking food for children.
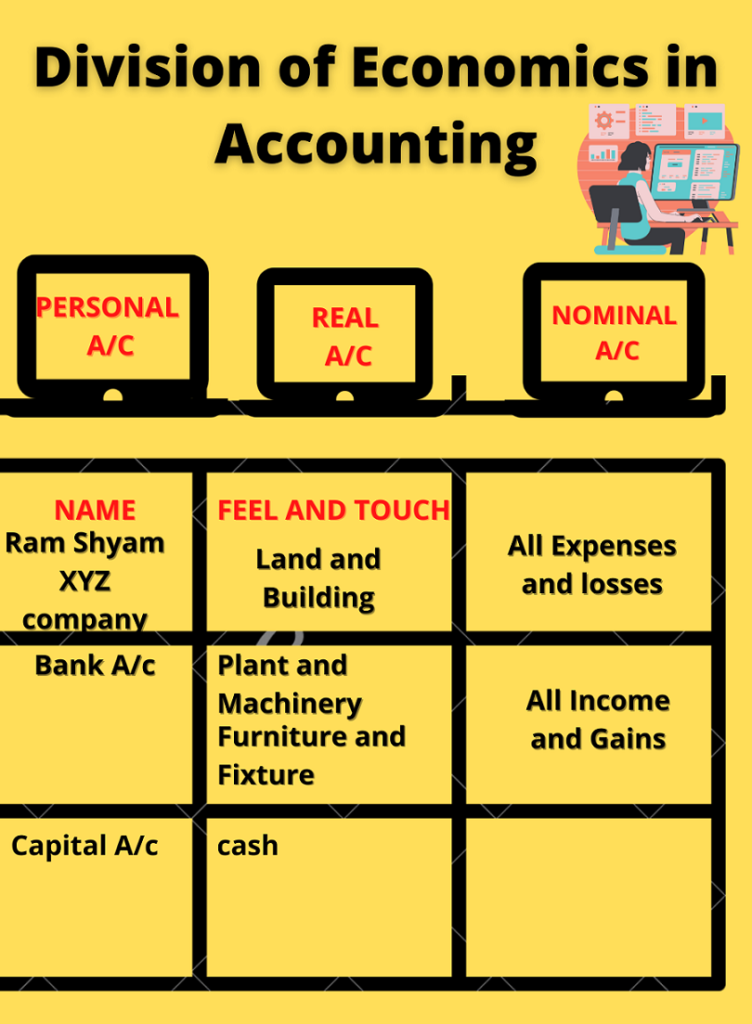
In accounting we only record Economic activities only. Therefore economic activities are considered in accounting hence we divide them into three parts as shown below.
Activities that involve money or the exchange of products or services are economic activities.
Business run for profit is example of economic activity.
Non-economic activity is an activity performed with the purpose of rendering services to others without any consideration to financial gain. Example Mother cooking food for children.
In accounting we only record Economic activities only. Therefore economic activities are considered in accounting hence we divide them into three parts as shown below.
PERSONAL ACCOUNTS (Name) | REAL ACCOUNTS (Feel and Touch) | NOMINAL ACCOUNTS (All expenses losses gain and income) |
|
|
|
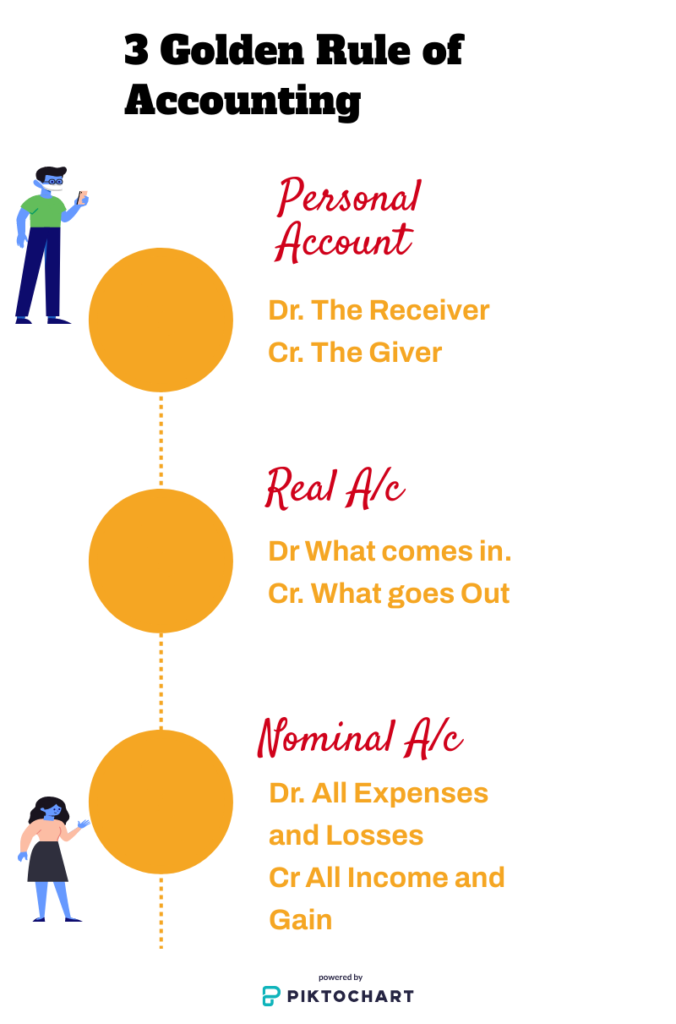
Three golden Rules of Accounting | |
| Personal A/c | Debit (Dr.) The receiver Credit (Cr.) The Giver |
| Real A/c | Debit (Dr.) What comes In Credit (Cr.) What Goes out |
| Nominal A/c | Debit (Dr.)All expenses and Losses Credit (Cr.) All gains and Income |
Application of how to make journal Entry
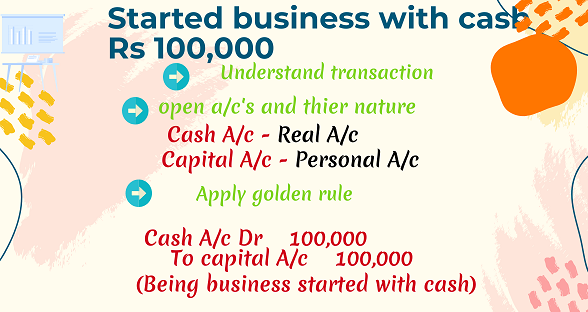
There are four (4) steps in the construction of a journal entry
|
| 1. Understanding the transaction. |
| 2. Identifying the accounts to be opened. |
3. Classifying the accounts as per the division of the economy. |
4. Applying the rules |
Before we go further, we understand that What is a Journal Entry?
A Journal Entry is commonly a summary of the debits and credits of the transaction entry to the Journal. Journal entries are important because they give us to sort our transactions into manageable data.
A journal entry is used to register a business transaction in the accounting records of a business. We usually record a journal entry in the Journal , quickly, it may be recorded in a subsidiary ledger that is then summed up and rolled forward into the general ledger. The general ledger is then used to create financial statements for the organization.
Example of Journal entry
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
Account Dr. To Account
| Xxxx | xxxx |
while making journal entry as we know we have identify the account and apply golden rule .
Capital A/c (Personal)
Cash A/c (Real A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Cash A/c Dr. | 100,000 | |
To Capital A/c ( Being business started with the cash) | 100,000 |
Bank A/c (P)
Cash A/c (R)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Bank A/c Dr. To cash A/c (being cash deposited into bank) | 50,000 | 50,000 |
(Note: when name is given in the transaction it means goods are purchased on credit from the party.)
Purchase A/c (Real A/c)
Mohan (Personal)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| Xxx | Purchase A/c Dr. To Mohan A/c (Being goods purchased from Mohan) | 9,000 |
9,000 |
Sales A/c (Real a/c)
Cash A/c ( Real A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| Xxx | Cash A/c Dr. To Sales A/c (being goods sold for cash)
| 9,000 |
9,000 |
5.Purchase goods by cheque Rs. 7000.
Purchase A/c (Real A/c)
Bank A/c (Personal a/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| Xxx | Purchase A/c Dr. To Bank A/c (being goods purchase by cheque) | 7,000 |
7,000 |
6.Sold goods by cheque Rs 9000.
Sale A/c (Real a/c)
Bank (Personal A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Bank A/c Dr To sales A/c .being goods sold by cheque) | 7,000 |
7,000 |
7.Sold goods from Ramesh Rs 3000.
Sale A/c (Real A/c)
Ramesh (Personal a/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| Xxx | Ramesh A/c Dr. To sales A/c (being goods purchase by cheque) | 3,000 |
3,000 |
8..Purchase Machinery for cash Rs. 20,000.
Machinery A/c (real A/c)
Cash a/c (real A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Machinery A/c Dr. TO Cash A/c. (being machinery purchased) | 20,000 |
20,000 |
9..Paid Rent Rs 8000.
Rent A/c (nominal A/c)
Cash A/c (real A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Rent A/c To Cash A/c (being rent paid) | 8,000 |
8,000 |
10..Received Commission Rs 800 by cheque.
Cash A/c ( Real A/c)
Commission (Nominal A/c)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Cash A/c To commission (being commission received) | 800 |
800 |
Meaning | Trade DiscountA discount given by the seller to the buyer as a deduction in the list price of the commodity is trade discount. | Cash DiscountA deduction in the amount of invoice allowed by the seller to the buyer in return for immediate payment is cash discount. |
| Purpose | To facilitate a bulk sales. | To facilitate a prompt payment. |
| Invoice | It is shown in invoice as a deduction itself. | It is not shown in invoice. |
When allowed? | Trade DiscountAt the time of purchase. | Cash DiscountAt the time of payment. |
| Allowed to all customers | Yes | No |
| Entry in books | No | Yes |
Format of Bill or invoice under Trade Discount . Here trade discount is shown in the bill but not
| S.NO | ITEM | PRICE | UNITS | TRADE DISCOUNT | AMOUNT |
| 1 | X | 100 | 100 | !0% | 9000 |
| Total amount | 9000/ |
Journal entry of trade discount Example:
10,000 X 10% = 1000
10,000 – 1000 = Rs 9000
Journal entry for the transaction will be
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
Purchase A/c Dr. To Mohan ( being goods purchased from Mohan)
| 9,000 |
9,000 |
2. Sold goods to Disha Rs 20,000 and trade discount allowed 10% .
20,000 X 10% = 2000
20000-2000= 18,000
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Disha Dr. . To Sales A/c ( being goods Sold to disha)
| 18,000 |
18,000 |
Journal entry of Cash discount .
Purchase Goods from Mahesh Rs 10,000
Purchase A/c (r)
Mahesh (P)
Purchase A/c 10,000
To Mahesh 10,000
(being goods purchased from Mahesh)
Paid cash to Mahesh Rs 9500 and received cash discount Rs 500.
cash discount is shown in the book of accounts.
Cash A/c (r )
Mahesh ( P)
Discount received ( N)
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Mahesh Dr.. . To cash A/c To discount received A/c ( being goods Sold to disha)
| 10,000 |
9,500 500 |
Sold goods to Varun Rs 20,000
Sale A/c (r)
Varun (p)
Varun Dr . 20,000
To sales A/c 20,000
(being goods sold to Varun)
Received cash from Varun Rs 19,500 and discount allowed 500
| Date | Particular | Amount | Amount |
| xxx | Cash A/c Dr. Discount Allowed A/c Dr. To Varun (being cash paid to Varun and discount allowed)
| 19,500 |
500 20,000 |
