
Table of Contents
ToggleLet’s begin with the fundamentals of while loops — how they work, when to use them, and why beginners often make mistakes.
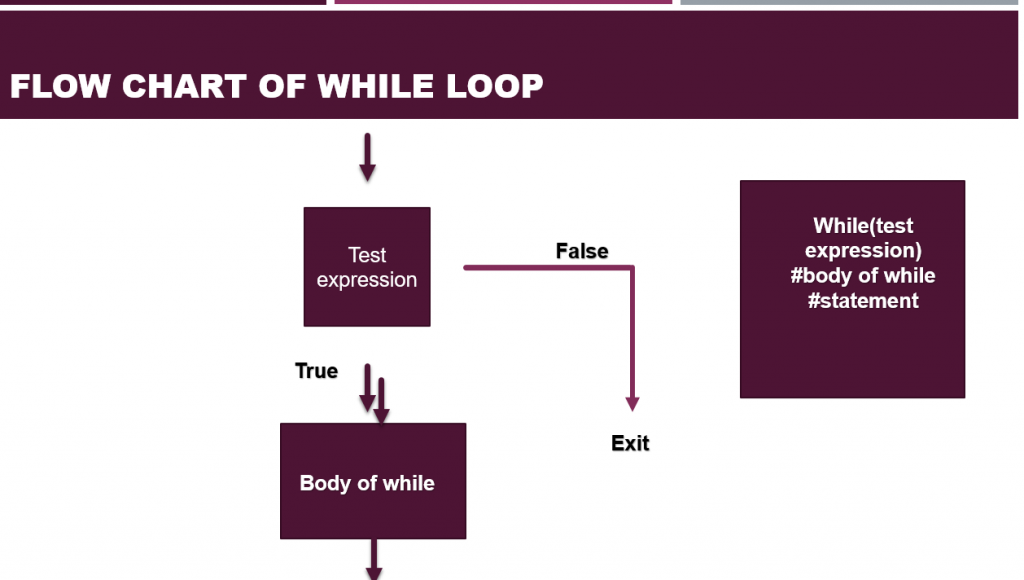
While loop executes a block of code as long as the test condition is True.
A control variable must be initialized before the loop starts, or the loop may not work.
The condition is checked before executing the loop body — called an entry-controlled loop.
You must update the variable inside the loop to avoid an infinite loop.
💡 Syntax:
while condition:
# block of code

In Python, a while loop executes a block of code repeatedly until a specified condition becomes False. When the condition is no longer true, the program exits the loop and continues execution.
⚠️ Note: If the condition always remains True and never changes, the loop becomes an infinite loop — it will never stop unless you break it manually.
i = 0).i < 5) is true.i += 1).False, exit the loop.
i = 1
while i <= 3:
print("Number:", i)
i += 1
# Output:
# Number: 1
# Number: 2
# Number: 3
Practice these real-world Python while loop programs to strengthen your fundamentals. These examples range from beginner to intermediate level, including sum, reverse, factorial, prime check, and more.
count = 1
while count <= 10:
print(count)
count += 1
📤 Output:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
n = 5
sum = 0
i = 1
while i <= n:
sum += i
i += 1
print("Sum =", sum)
📤 Output: Sum = 15
num = 7
i = 2
flag = 0
while i < num:
if num % i == 0:
flag = 1
break
i += 1
if flag == 0:
print(num, "is a prime number")
else:
print(num, "is not a prime number")
📤 Output: 7 is a prime number
count = 0
while count < 3:
print("Vista Academy Data Science Institute")
count += 1
📤 Output:
Vista Academy Data Science Institute
Vista Academy Data Science Institute
Vista Academy Data Science Institute
number = 3
i = 1
while i <= 10:
print(f"{number} x {i} = {number * i}")
i += 1
📤 Output:
3 x 1 = 3
3 x 2 = 6
3 x 3 = 9
3 x 4 = 12
3 x 5 = 15
3 x 6 = 18
3 x 7 = 21
3 x 8 = 24
3 x 9 = 27
3 x 10 = 30
num = 1234
reverse = 0
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
reverse = (reverse * 10) + digit
num //= 10
print("Reversed number:", reverse)
📤 Output: Reversed number: 4321
def factorial(n):
if n < 0:
return "Not defined"
elif n == 0 or n == 1:
return 1
else:
fact = 1
i = 2
while i <= n:
fact *= i
i += 1
return fact
number = 5
print("Factorial:", factorial(number))
📤 Output: Factorial: 120
count = 0
num = 2
primes = []
while count < 10:
is_prime = True
i = 2
while i*i <= num:
if num % i == 0:
is_prime = False
break
i += 1
if is_prime:
primes.append(num)
count += 1
num += 1
print("First 10 primes:", primes)
📤 Output: First 10 primes: [2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29]
n = 10
i = 2
while i <= n:
print(i)
i += 2
📤 Output: 2
4
6
8
10
num = 456
sum = 0
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
sum += digit
num //= 10
print("Sum of digits:", sum)
📤 Output: Sum of digits: 15
a = 48
b = 18
while b != 0:
a, b = b, a % b
print("GCD is:", a)
📤 Output: GCD is: 6
num = 67891
count = 0
while num != 0:
num //= 10
count += 1
print("Total digits:", count)
📤 Output: Total digits: 5
num = 153
temp = num
sum = 0
while temp > 0:
digit = temp % 10
sum += digit ** 3
temp //= 10
if num == sum:
print("Armstrong Number")
else:
print("Not an Armstrong Number")
📤 Output: Armstrong Number
n = 7
a, b = 0, 1
i = 0
while i < n:
print(a, end=" ")
a, b = b, a + b
i += 1
📤 Output: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8
num = 968421
smallest = 9
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
if digit < smallest:
smallest = digit
num //= 10
print("Smallest digit:", smallest)
📤 Output: Smallest digit: 1
num = 121
original = num
reverse = 0
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
reverse = (reverse * 10) + digit
num //= 10
if original == reverse:
print("Palindrome Number")
else:
print("Not a Palindrome")
📤 Output: Palindrome Number
ch = 65
while ch <= 90:
print(chr(ch), end=" ")
ch += 1
📤 Output: A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
base = 3
exp = 4
result = 1
while exp > 0:
result *= base
exp -= 1
print("Result:", result)
📤 Output: Result: 81
num = 2846
sum = 0
while num > 0:
digit = num % 10
if digit % 2 == 0:
sum += digit
num //= 10
print("Sum of even digits:", sum)
📤 Output: Sum of even digits: 10
text = "Data Science"
i = 0
count = 0
while i < len(text):
if text[i].lower() in 'aeiou':
count += 1
i += 1
print("Total vowels:", count)
📤 Output: Total vowels: 5
Test your knowledge by selecting the correct answer. You’ll get instant feedback!
i = 1
while i < 5:
print(i)
i += 1
✅ Correct! This prints numbers from 1 to 4.
✅ Correct! It runs until the condition is false.
x = 10
while x > 5:
print(x)
x -= 2
✅ Correct! It prints 10, 8, 6 and stops.
✅ Correct! Forgetting to change the variable keeps loop running forever.
i = 1
while i < 6:
print(i)
i += 1
✅ Correct! Last printed number is 5.
i = 1
while i <= 3:
print("Python")
i += 1
✅ Correct! It prints "Python" three times.
i = 10
while i >= 1:
print(i)
✅ Correct! It loops forever as i isn't updated.
break in a while loop?✅ Correct! break ends the loop execution instantly.
i = 0
while i < 3:
print(i)
i += 1
✅ Correct! It prints 0, 1, 2 — then stops.
x = 5
while x > 0:
print(x)
x = x + 1
✅ Correct! x increases, so the loop never ends.
x = 0
while x < 3:
x += 1
print(x * "*")
✅ Correct! It prints increasing asterisks each time using string multiplication.
✅ Yes! The while loop continues only as long as the condition remains True.
i = 10
while i > 5:
print(i, end=" ")
i -= 2
✅ Correct! It decreases by 2 until i becomes ≤ 5.
✅ Exactly! break exits the loop instantly.
✅ Great! while True: runs forever unless a break condition is included.
x = 5
while x > 0:
print(x, end=" ")
x -= 1
✅ Correct! Loop prints and decrements x until it becomes 0.
✅ Right! Without a false condition, while loop goes on forever.
✅ Perfect! continue skips to the next loop iteration.
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(i**2)
i += 1
✅ Correct! It prints the square of each number from 1 to 5.
✅ Yes! If the loop variable is not updated, it may never terminate.
A while loop is a control flow statement that repeatedly executes a block of code as long as the given condition is True.
An infinite while loop runs endlessly because the condition never becomes False. For example: while True: will run forever unless stopped by a break statement.
Always make sure the condition inside your while loop can eventually become False. Update your loop variable inside the loop to avoid infinite repetition.
Yes! Python allows using an else block with while loop, which runs only when the condition becomes False naturally (not interrupted by break).
You can use a counter variable (like i = 0) and increment it on each iteration to track how many times the loop runs.
– Forgetting to update the loop variable
– Wrong indentation
– Using = instead of ==
– Creating an infinite loop accidentally
Yes, break is used to exit the loop early, and continue is used to skip the current iteration and move to the next one.
while condition:
statement(s)
Example:
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
Vista Academy’s Master Program in Data Science offers in-depth training in advanced topics such as machine learning, artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and predictive modeling. Gain hands-on experience with Python, R, SQL, and TensorFlow to build a strong foundation for your career in data science.
Address: Vista Academy, 316/336, Park Rd, Laxman Chowk, Dehradun, Uttarakhand 248001
