Key Difference Between Data Science and Data Analytics to Know
Table of Contents
ToggleDATA SCIENCE AND DATA Analytics are Buzzword
Data science and Data Analytics becomes popular during a time.
Today, data is the new oil for businesses to gather critical insights and improve business performance to grow in the market.
As per Economic Forum that by the end of 2020, the daily global data generation will reach 44 zettabytes. By 2025, this number will reach 463 exabytes.
of data!.
Big Data includes everything – texts, emails, tweets, user searches (on search engines), social media chatter, data generated from IoT and connected devices – basically, everything we do online.
The data generated every day via the digital world is so vast and complex that traditional data processing and analysis systems cannot handle it.Thus the role of Data science and Data Analytics comes.
Data analysts and data scientists represent two of the most in-demand, high-paying jobs in 2021. This exponential growth has led organizations of all sizes to wonder how they can leverage information to realize business benefits.
Both data analysts and data scientists work with data
Both data analysts and data scientists work with data, but they do so in different ways.
One of the biggest differences between data analysts and scientists is what they do with data.
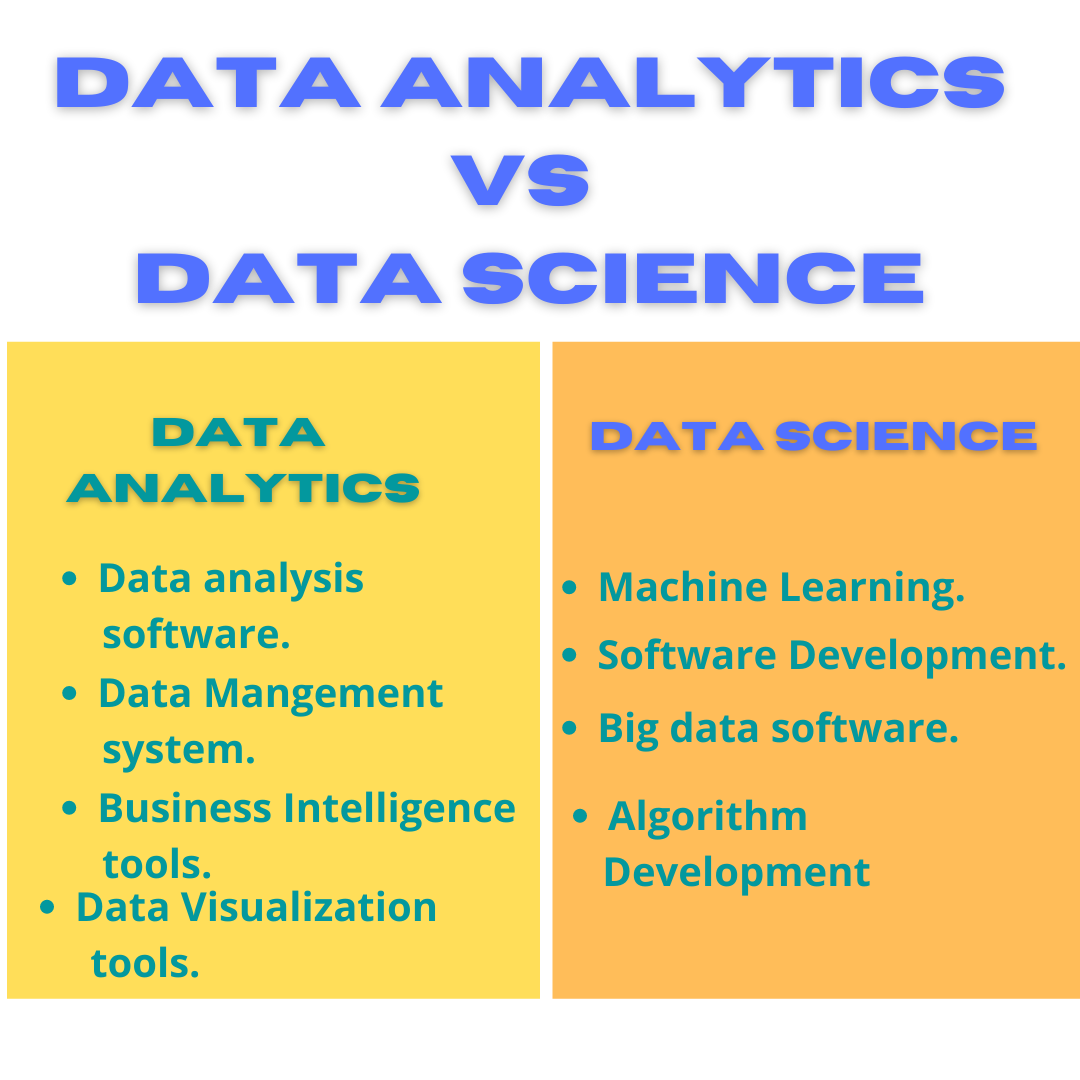
Responsibilities of Data Analysts
Data analytics refers to the process and practice of analyzing data to answer questions, extract insights, and identify trends. This is done using an array of tools, techniques, and frameworks that vary depending on the type of analysis being conducted.
Data analysts typically work with structured data to solve tangible business problems using tools like SQL, R or Python programming languages, data visualization software, and statistical analysis. Common tasks for a data analyst might include:
- Obtain data from primary and secondary sources
- Corporate and get together with organizational leaders to identify informational needs
- Experiment with different analytical tools like predictive analytics, prescriptive analytics, descriptive analytics, and diagnostic analytics.
- Cleaning and re managing data for analysis
- Presenting findings in an easy-to-understand way to inform data-driven decisions.
Responsibilities of Data Scientists
Whereas data analytics is primarily focused on understanding datasets and gleaning insights that can be turned into actions, data science is centered on building, cleaning, and organizing datasets. Data scientists create and leverage algorithms, statistical models, and their own custom analyses to collect and shape raw data into something that can be more easily understood.
- To Gathering, cleaning, and processing raw data.
- To perform Exploratory Data Analysis on large datasets.
- To perform data mining by creating ETL pipelines.
- To perform statistical analysis using ML algorithms like logistic regression, KNN, Random Forest, Decision Trees, etc.
- To write code for automation and build resourceful ML libraries.
- To glean business insights using ML tools and algorithms.
- To identify new trends in data for making business predictions.