Unlocking Business Insights: SQL Analysis of Sales and Revenue
Table of Contents
ToggleProject Overview:
This project focuses on analyzing sales and revenue data to gain valuable insights into a business’s performance. The project utilizes a set of SQL tables to store and manage sales transactions, product information, customer details, and, optionally, date and region data for comprehensive analysis.
1. Data Structure:
The project involves the creation of several SQL tables:
- sales:
Stores detailed information about individual sales transactions, including product, customer, date, and revenue data.
- products:
contains product-related information, such as names, categories, and pricing.
- customers:
Stores customer details for segmentation and analysis.
- dates (optional):
Provides date-related data for time-based analysis.
- regions (optional):
Includes regional data for geographic analysis.
Creating Tables in Sql
-- Create a table for sales transactions
CREATE TABLE sales (
sale_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_id INT,
customer_id INT,
sale_date DATE,
quantity INT,
unit_price DECIMAL(10, 2),
sales_amount DECIMAL(12, 2)
);
-- Create a table for products
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR(255),
category VARCHAR(50),
unit_cost DECIMAL(10, 2),
unit_price DECIMAL(10, 2)
);
-- Create a table for customers
CREATE TABLE customers (
customer_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name VARCHAR(255),
email VARCHAR(255),
phone VARCHAR(20),
city VARCHAR(100),
state VARCHAR(50),
country VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Optionally, create a table for dates (to track sales by date)
CREATE TABLE dates (
date_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
sale_date DATE,
day_of_week VARCHAR(15),
month VARCHAR(15),
quarter VARCHAR(15),
year INT
);
-- Optionally, create a table for regions (to track sales by region)
CREATE TABLE regions (
region_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
region_name VARCHAR(100),
state VARCHAR(50),
country VARCHAR(50)
);
Insert data in each table
Insert in Sales Table
-- Insert data into the 'sales' table
INSERT INTO sales (sale_id, product_id, customer_id, sale_date, quantity, unit_price, sales_amount)
VALUES
(1, 1, 1, '2023-01-15', 2, 50.00, 100.00),
(2, 2, 2, '2023-01-20', 3, 40.00, 120.00),
(3, 3, 3, '2023-02-10', 1, 75.00, 75.00),
(4, 1, 4, '2023-02-15', 4, 55.00, 220.00),
(5, 2, 5, '2023-03-05', 2, 45.00, 90.00),
(6, 3, 6, '2023-03-15', 3, 70.00, 210.00),
(7, 1, 7, '2023-04-10', 5, 60.00, 300.00),
(8, 2, 8, '2023-04-20', 1, 35.00, 35.00),
(9, 3, 9, '2023-05-05', 2, 65.00, 130.00),
(10, 1, 10, '2023-05-20', 3, 70.00, 210.00);
Insert in Product Table
-- Insert data into the 'products' table
INSERT INTO products (product_id, product_name, category, unit_cost, unit_price)
VALUES
(1, 'Product A', 'Electronics', 40.00, 80.00),
(2, 'Product B', 'Clothing', 20.00, 50.00),
(3, 'Product C', 'Home & Garden', 50.00, 100.00),
(4, 'Product D', 'Electronics', 60.00, 120.00),
(5, 'Product E', 'Clothing', 25.00, 50.00),
(6, 'Product F', 'Home & Garden', 35.00, 80.00),
(7, 'Product G', 'Electronics', 45.00, 90.00),
(8, 'Product H', 'Clothing', 22.00, 55.00),
(9, 'Product I', 'Home & Garden', 55.00, 110.00),
(10, 'Product J', 'Electronics', 65.00, 130.00);
Inserting Data into the customers Table:
-- Insert data into the 'customers' table
INSERT INTO customers (customer_id, customer_name, email, phone, city, state, country)
VALUES
(1, 'John Smith', 'john@example.com', '555-123-4567', 'New York', 'NY', 'USA'),
(2, 'Jane Doe', 'jane@example.com', '555-987-6543', 'Los Angeles', 'CA', 'USA'),
(3, 'David Johnson', 'david@example.com', '555-555-5555', 'Chicago', 'IL', 'USA'),
(4, 'Emily Brown', 'emily@example.com', '555-222-3333', 'San Francisco', 'CA', 'USA'),
(5, 'Michael Wilson', 'michael@example.com', '555-444-7777', 'Houston', 'TX', 'USA'),
(6, 'Sarah Davis', 'sarah@example.com', '555-666-9999', 'Miami', 'FL', 'USA'),
(7, 'Robert Miller', 'robert@example.com', '555-777-1111', 'Seattle', 'WA', 'USA'),
(8, 'Lisa Jones', 'lisa@example.com', '555-888-2222', 'Atlanta', 'GA', 'USA'),
(9, 'William Lee', 'william@example.com', '555-999-3333', 'Boston', 'MA', 'USA'),
(10, 'Mary Taylor', 'mary@example.com', '555-111-4444', 'Denver', 'CO', 'USA');
Inserting Data into the dates Table
-- Insert data into the 'dates' table
INSERT INTO dates (date_id, sale_date, day_of_week, month, quarter, year)
VALUES
(1, '2023-01-15', 'Sunday', 'January', 'Q1', 2023),
(2, '2023-01-20', 'Friday', 'January', 'Q1', 2023),
(3, '2023-02-10', 'Thursday', 'February', 'Q1', 2023),
(4, '2023-02-15', 'Wednesday', 'February', 'Q1', 2023),
(5, '2023-03-05', 'Sunday', 'March', 'Q1', 2023),
(6, '2023-03-15', 'Wednesday', 'March', 'Q1', 2023),
(7, '2023-04-10', 'Monday', 'April', 'Q2', 2023),
(8, '2023-04-20', 'Thursday', 'April', 'Q2', 2023),
(9, '2023-05-05', 'Friday', 'May', 'Q2', 2023),
(10, '2023-05-20', 'Saturday', 'May', 'Q2', 2023);
Inserting Data into the regions Table
-- Insert data into the 'regions' table
INSERT INTO regions (region_id, region_name, state, country)
VALUES
(1, 'Northeast', 'NY', 'USA'),
(2, 'West Coast', 'CA', 'USA'),
(3, 'Midwest', 'IL', 'USA'),
(4, 'South', 'TX', 'USA'),
(5, 'Southeast', 'FL', 'USA'),
(6, 'Pacific Northwest', 'WA', 'USA'),
(7, 'Southeast', 'GA', 'USA'),
(8, 'Northeast', 'MA', 'USA'),
(9, 'Mountain West', 'CO', 'USA'),
(10, 'Northeast', 'CT', 'USA');
Data Analysis:
The project encompasses various data analysis tasks, including but not limited to:
- Calculating total revenue over specific time periods.
- Analyzing sales trends over time, identifying seasonal patterns.
- Assessing product performance, including best-sellers and profit margins.
- Segmenting customers based on behavior, demographics, and geography.
- Examining sales by region to understand geographic variations.
list of all the tables Command
SHOW TABLES;
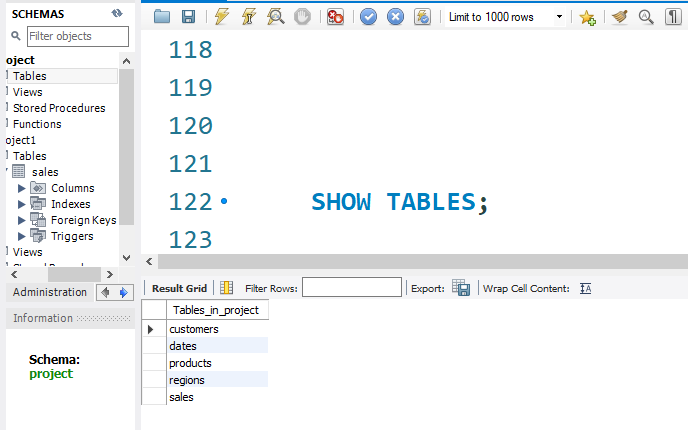
Select table to see the tables
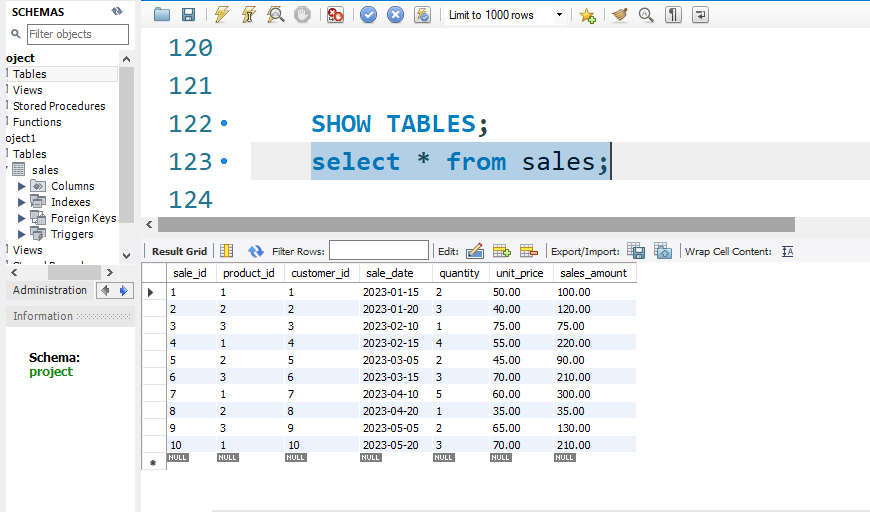
select * from customers;simialry you can select others tables and check rows and columns
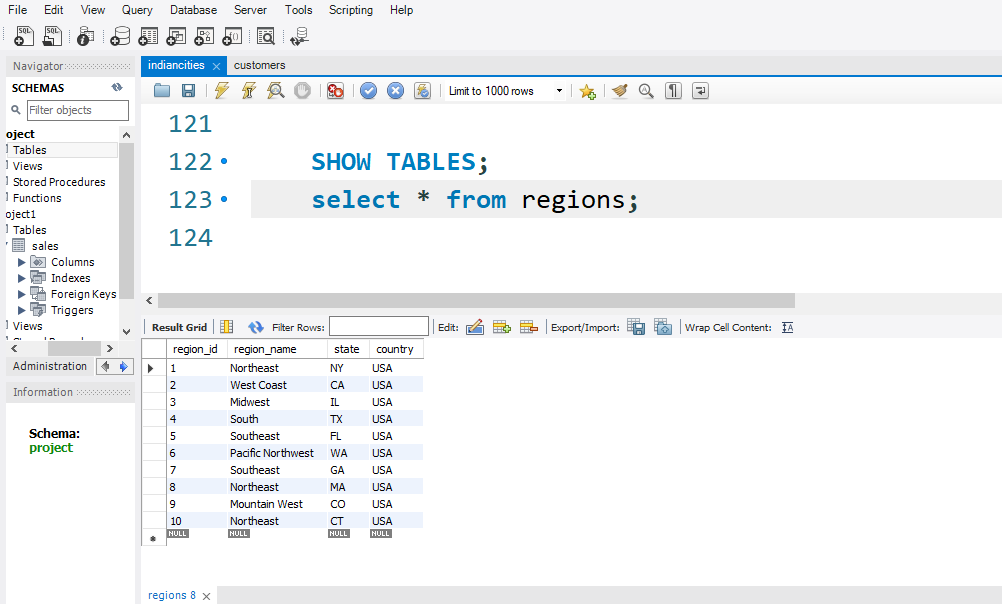
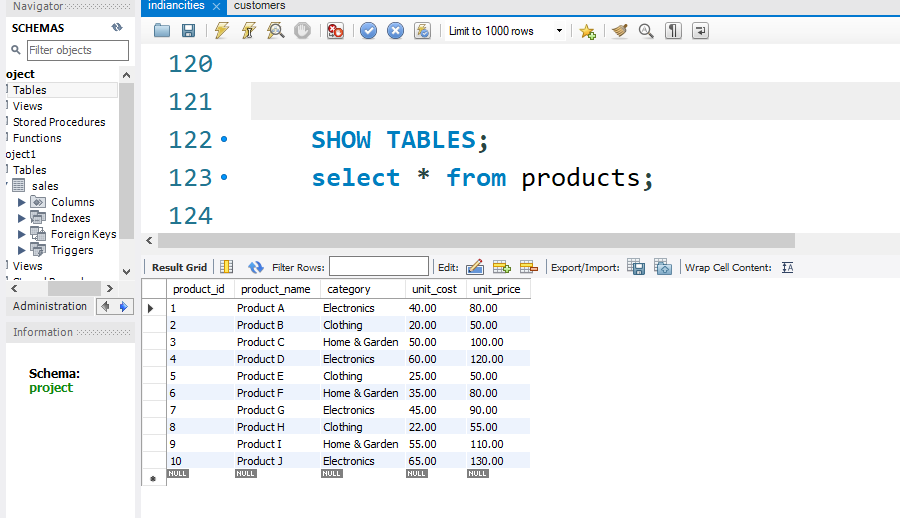
Total sales BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-03-31'
SELECT SUM(sales_amount) AS total_revenue FROM sales WHERE sale_date BETWEEN '2023-01-01' AND '2023-03-31';
Top-Selling Products:
SELECT product_id, SUM(quantity) AS total_sold FROM sales GROUP BY product_id ORDER BY total_sold DESC LIMIT 5;
3. Customer Segmentation:
SELECT customer_id, SUM(sales_amount) AS total_spent FROM sales GROUP BY customer_id HAVING total_spent > 1000;

