What is trading Accounts in Accounting and its Format
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Trading Accounts ?
Trading accounts is first part of Income statement .It shows either Gross Profit or Gross Loss.
The Gross Profit or Gross Loss is then transfer to Profit and Loss Accounts which is secound part of Income statement .
Now We can say that Trading accounts is prepared to calculate gross profit and gross loss which incurred due to trading activities in business.
If the amount of sales of goods or service in a particular period exceeds the amount of purchase and the expenses directly connected with such purchases the difference is termed as Gross profit. On the other hand if the purchases and direct expense exceed the sale the difference is called gross loss.
Trading accounts includes all direct expenses .
According to J.R Batuboi ” The trading accounts shows the result of buying and selling of goods .In preparing this account the general establishment charges are ignored and only the transaction in goods are included”
Trading Accounts shows all the transaction relating to goods purchases and we can say all expense till sale of goods
Why to prepare Trading Accounts ?
Some point to know why to prepare Trading Account.
1) Trading Account help to find out Gross profit and loss.
Trading account gives information about gross profit or gross loss made by the firm in a particular financial year, which results from buying or selling of goods during a particular financial year.
It helps to analyze and compare the gross profit or gross loss to two financial years .Thus gives us information for improvement .
2) Trading Account Gives information of Closing stock
Closing stock has to be valued and recorded in a trading account. We can compare this stock with the closing stock of the previous year and if the stock shows an increasing trend the reason may be to consideration.
3) Trading accounts provide information about the direct expenses
They recorded all the expenses incurred on the purchase and manufacturing of goods in the trading account in a summarized form and are also known as direct expense .
Percentage of such expense on sales can be calculated compared and analysis with those of previous year .It help to control the expense .
4) It provides safety against possible losses .
If the ratio of gross profit has decreased in comparison to the preceding year the businessman can take effective measures to safeguard himself against future losses.
For example, he may increases the sale price of his goods or may proceed to analyze and control the direct expense.
How to prepare trading account ?
The trading account is prepared by debiting opening stock, purchases less returns, direct expenses and crediting sales less returns, and closing stock.
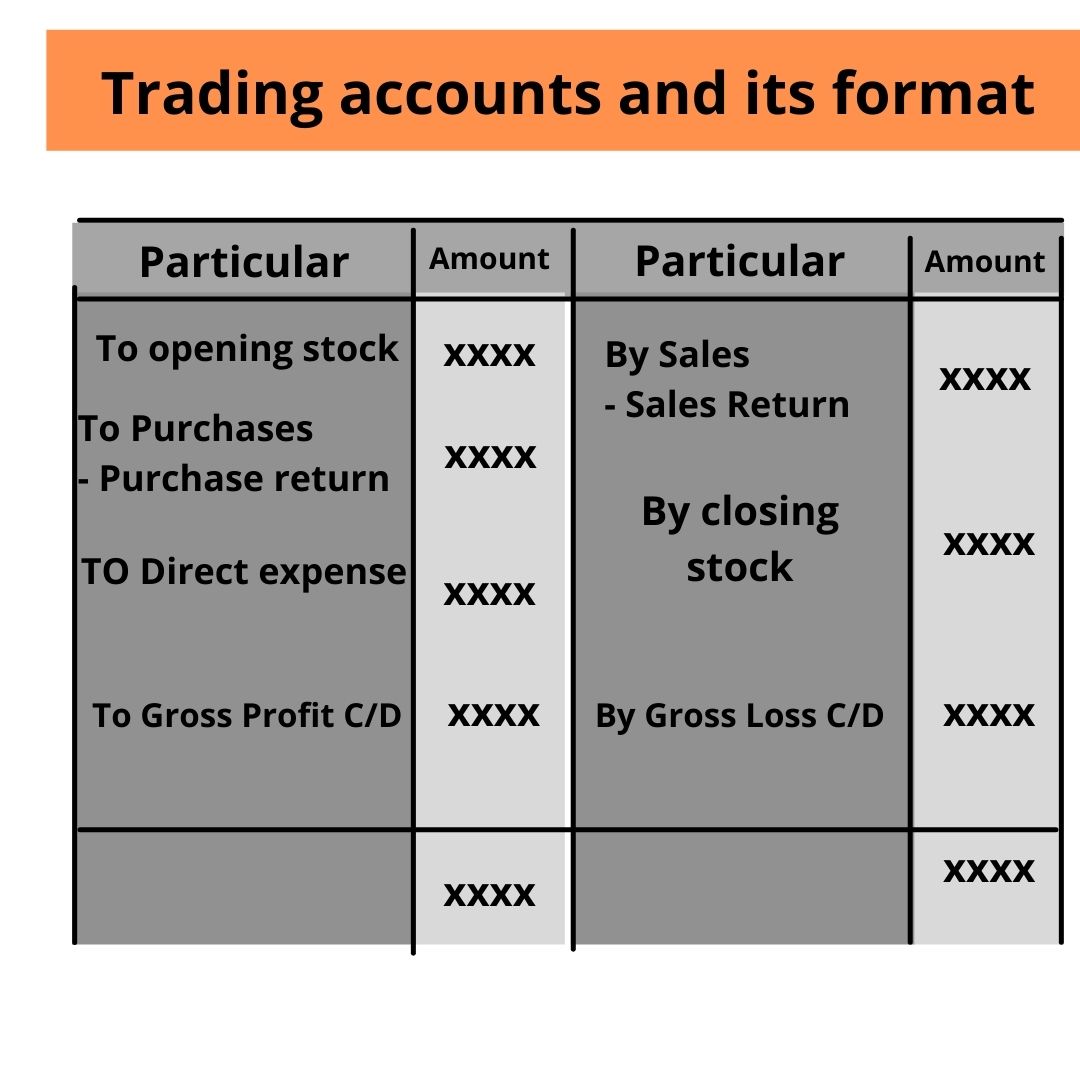
Trading Account Format
Trading accounts for the year ending ………….
Particular Dr. | Amount | Particular Cr. | Amount |
To opening stock | Xxxx | By sales – Sales Return (return Inward) | Xxx |
To Purchase -Purchase Return / Return Inward | Xxxxxx | By closing stock | XXX |
To wages |
|
|
|
To wages and salaries | Xxxx |
|
|
To carriage or carriage inward | Xxx |
|
|
To carriage of purchase | Xxx |
|
|
To gas fuel and power | Xxx |
|
|
To freight ,octroi and cartage | Xxx |
|
|
To manufacturing expense | xxx |
|
|
To factory lighting | Xxx |
|
|
To productive expense | Xxx |
|
|
To Royalty | Xxx |
|
|
To Custom duty | Xx |
|
|
To dock charges | xxx |
|
|
|
|
|
|
To Gross profit C/d | xxx | By Net Loss C/d | Xxx |
| Xxxx |
| xxxx |
|
|
|
|
Item in Debit side of Trading Accounts
Item written on the Debit side of Trading Accounts
Opening Stock :
Opening stock is the stock which carried forward from the last year of goods remain unsold .This is closing stock of last year and this year it is opening stock .
It may include
a) Raw material
b) Semi-finished goods
c) Finished goods.
2.Purchase Accounts :
Purchase accounts include all goods purchase during the year for resale .They are expense by nature and direct expense for firm,
2) Purchase return Account:
It include means goods once purchased are return to its supplier .Purchase return is given in the credit side of Trial balance .Purchase return is deducted from purchase .
3. Direct Expenses :
All direct expenses are to be written in the debit side of trading accounts as it contain information of expenses relating to goods purchased means bring them to godown and converting them into finished goods.
a) Wages : Wages are given to worker who are directly engaged in loading, unloading and production of goods.
b)Carriage or Carriage on purchase : When goods are bring to the godwon by truck ,train etc the freight paid to bring such goods are known as Carriage or carriage on Purchase.
c) Manufacturing Expense : Expenses incurred while converting raw material into fished goods are terms of manufacturing expenses.
d) Dock charges:
Dock charges are charges levied on ships and cargo who used to bring goods through ships from other destination .When dock charges are paid. They are expense for the organization that need to be shown in trading accounts in the books of accounts.
e) Import duty or custom duty :
When goods or raw material of goods are purchased from other country, then government imposes tax which is import duty that we need to show in trading account which is direct expense.
f)Octroi :
The local body of the district or state levied this when goods enter the city and hence debited the trading accounts.
g) Royalty
This the amount paid to the owner of mine or patent for using his right or patent. It charged royalty in trading accounts because it increases the cost of production because it need to be paid to its owner.
Item in Credit side of Trading Accounts
Item written on the credit side of trading accounts
- Sales Account
They showed sales account in the credit side of the trading account and it is direct income for the firm. It includes both cash and credit sales.
2 .Sales Retun
The goods once sold are returned by the customer is known as Sales return. We deduct sales return from sales on the credit side of the trading account .we write Sales return on credit side of trial balance.
Closing Stock :
The goods remain unsold during the year is known as closing stock.
They value closing stock at cost price or market value, whichever is higher.
The closing stock includes closing stock of raw material , semi-finished goods and finished goods.
It is generally given outside trial balance .The valuation of closing stock when accounts are closed. It is incorporated in accounts after passing adjustment journal entry .
Closing stock a/c
To Trading A/c
(closing stock transfer to Trading accounts)
Point to remember while preparing trading account
- We value the closing stock at cost or market price, whichever is less.
- However, firstly, we need to show the amount of closing stock on the income side of Trading account and secondly, in the balance sheet under current asset.
- On the date of preparation of trading account, we value the Closing stock which is physically available
Q&A
A trading account in accounting is a financial statement that summarizes the buying and selling activities of a business related to its core operations. It focuses on revenue from sales, cost of goods sold, and the resulting gross profit or loss.
The trading account includes two main components: sales revenue and the cost of goods sold. Sales revenue represents the total value of goods or services sold during a specific period, while the cost of goods sold represents the direct costs associated with producing or purchasing those goods.
The gross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the sales revenue. The formula is: Gross Profit = Sales Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold.
Businesses that deal in the buying and selling of physical goods, such as retailers and wholesalers, commonly use trading accounts to analyze their sales and cost of goods sold to determine their gross profit or loss.
The trading account provides valuable insights into a business’s core operational performance. It helps assess the efficiency of buying and selling activities, and the resulting gross profit indicates the profitability of these activities before considering other operating expenses.
The cost of goods sold is calculated by adding the beginning inventory to purchases made during the period and then subtracting the ending inventory. The formula is: Cost of Goods Sold = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory.
The trading account is a part of the income statement. The gross profit calculated in the trading account is then carried over to the income statement as the first line, followed by other operating revenues and expenses to determine the net profit or net loss.